Heat capacity determination
Heat capacity determination explained With our DSC the heat capacity of your material can be determined. The heat capacity is a measure of how much energy a material can absorb in order to heat it up by 1 Kelvin. Modulated DSC scans with sapphire as a reference material allows us to determine the heat capacity […]
Hot stage microscopy (HSM)
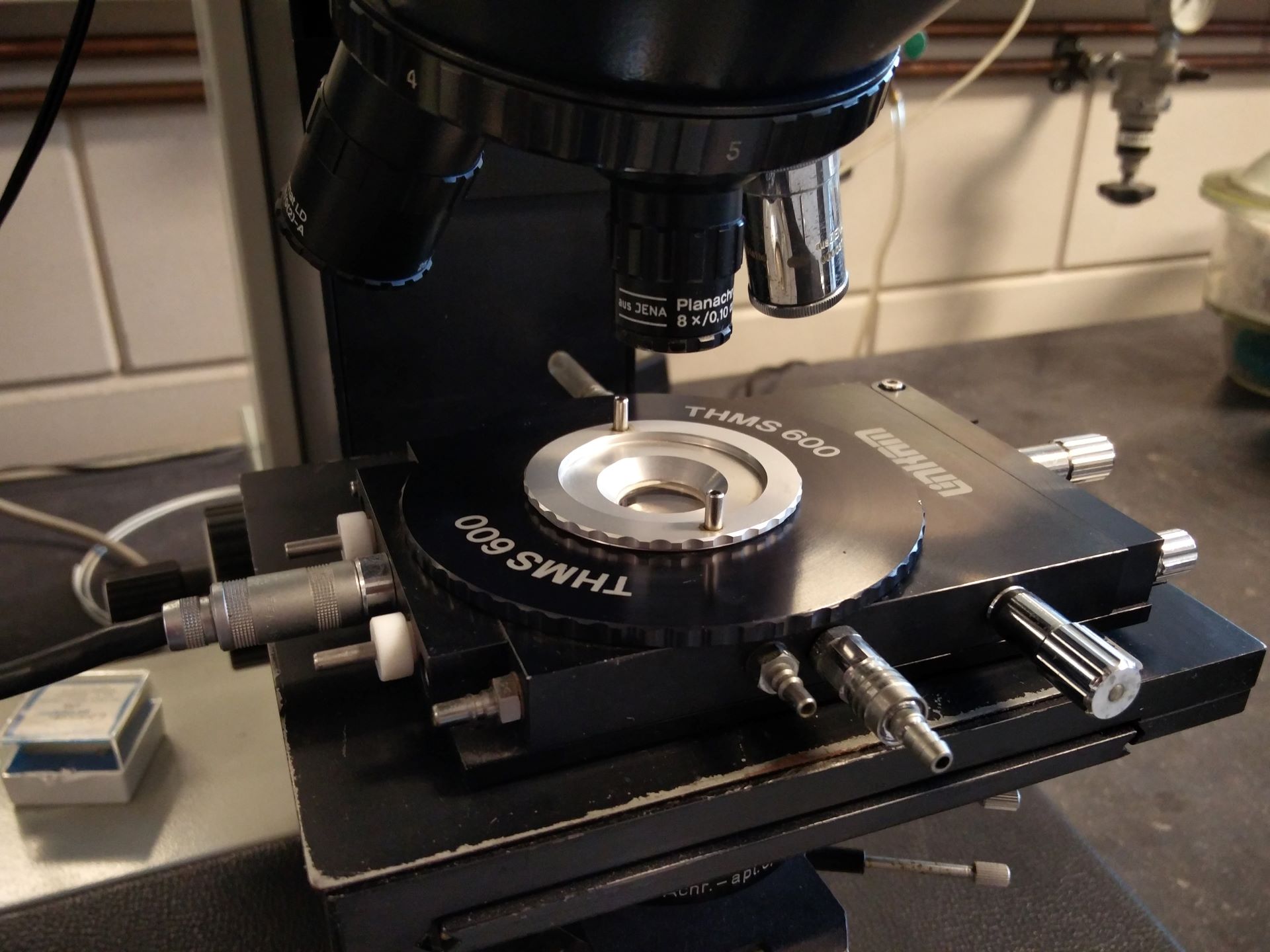

Hot stage microscopy explained Hot-stage microscopy (HSM), is a combination of microscopy and thermal analysis. It enables us to study polymers at high magnifications and elevated temperatures. This way we can actually see crystallization and melting processes. Also, particle size, particle morphology and crystallization kinetics can be determined with the addition of polarization filters. Our […]
Isothermal DSC
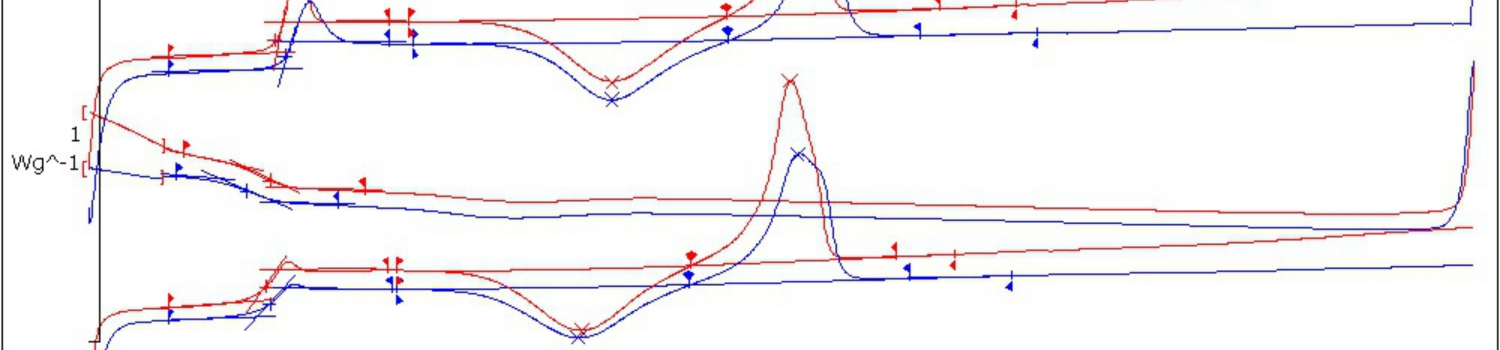
Isothermal DSC explained Besides standard DSC and hyper DSC we also offer isothermal DSC. This method heats up a polymer sample to a predefined temperature and keeps the sample at that temperature for a certain amount of time. This procedure can be conducted at different temperatures and is followed by Avrami analyses. This analysis when […]
DMA – Dynamic mechanical analysis
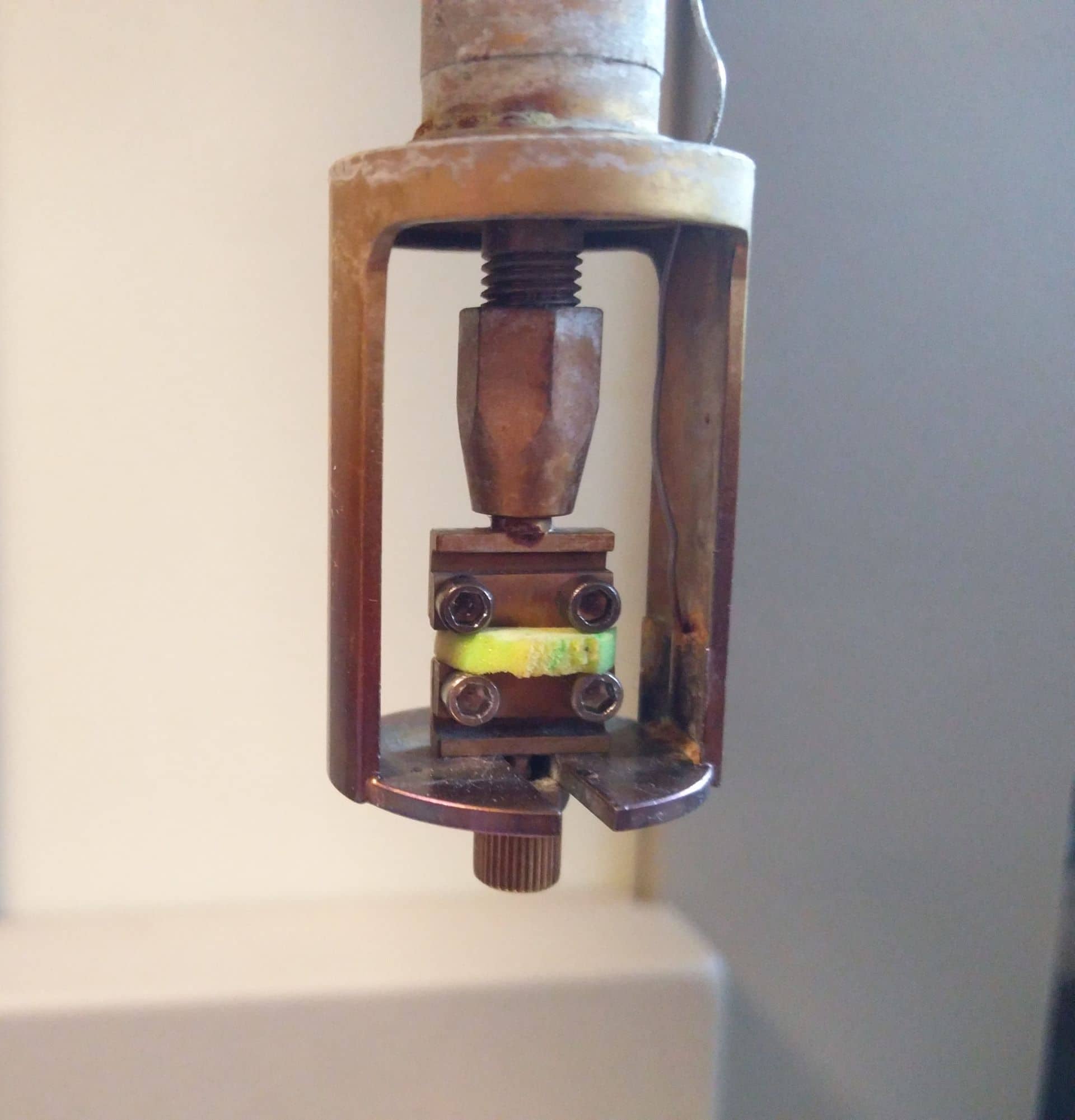

DMA explained A SEIKO Dynamic mechanical spectrometer Extar 6100 is available to you at Senbis Polymer Innovations. The DMA can be used for research on the viscoelastic behavior of polymer specimen. The DMA is able to apply a defined oscillatory force to a test specimen, the strain or displacement is subsequently measured. Typical parameters that […]
TNF measurements (temperature nuclei free)
TNF measurements explained TNF is the abbreviation for temperature nuclei free, which can be further defined as the temperature at which no crystals are present in a polymer melt. Even at temperatures above melting temperature persistent crystals may be present which can disturb processing techniques such as melt spinning. This measurement is also usefull for […]
Hyper DSC (up to 500K/min)

Hypers DSC explained Our hyper DSC, used for measuring polymeric samples by using very high heating and cooling rates, allows to spot transitions easier. Another practical application of this method is heating crystalline polymers above the temperature nuclei free (TNF) and quench it so an amorphous solid is obtained. This amorphous state can then be […]
Shrink force, (R)HASF
Shrink force, (R)HASF explained The shrink force of yarns can be measured according to ASTM D 5591-02. Within this test methode the force needed for a specific yarn shrinkage is measured over time. All measurements are standard done at 4 specimen (n=4) and average values are reported.
Hot water shrinkage (HWS)
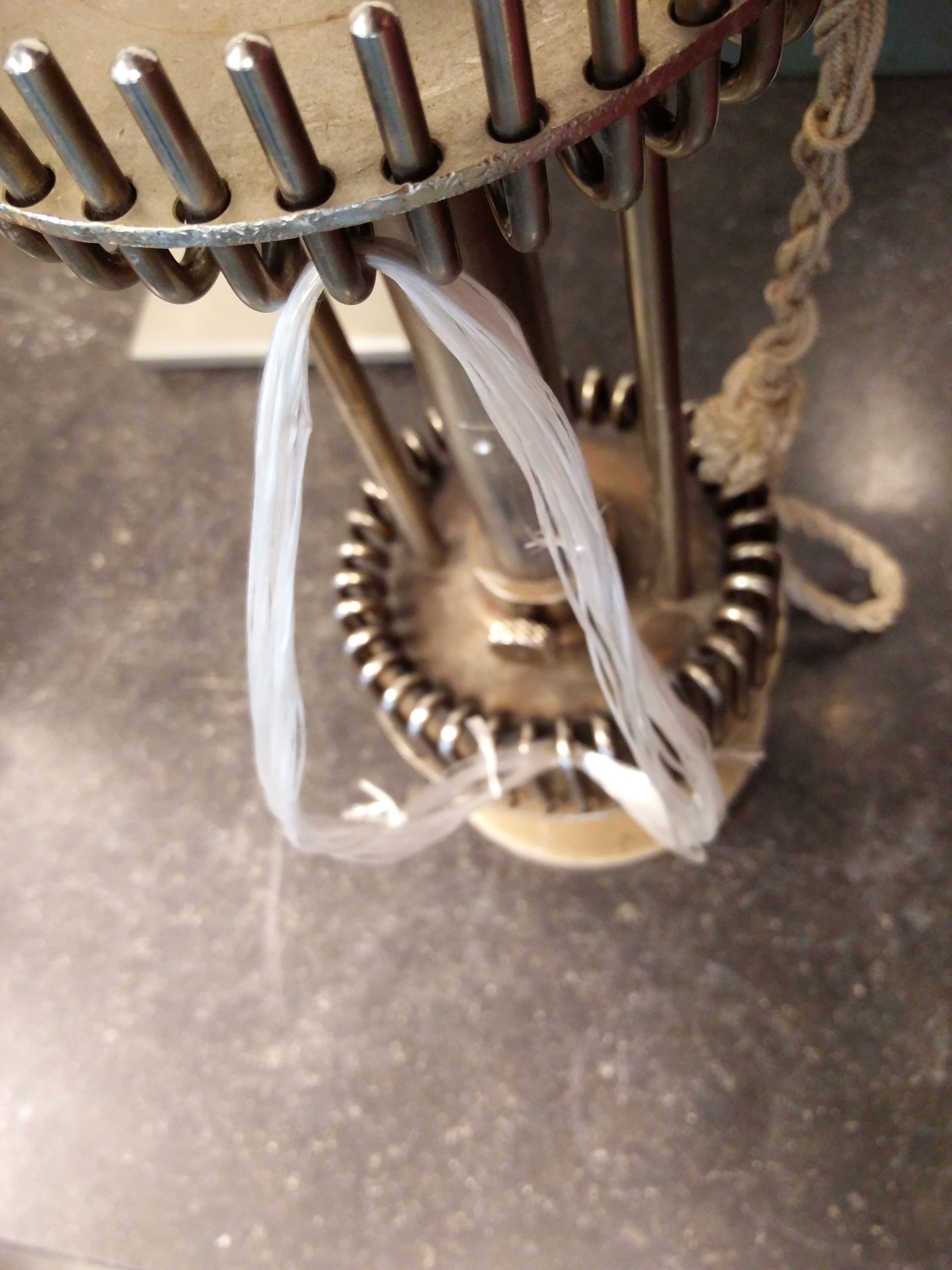

Hot water shrinkage (HWS) explained The hot water shrinkage test can be done at 90°C and 100 °C of yarns according to BISFA 2004 Ch 11 or ASTM D 4974-022. A normal procedure for PET yarns is 30 minutes at 90°C or 100°C. Usually, the average of four measurement samples are reported. Of course measurements can […]
Hot air shrinkage (HAS)
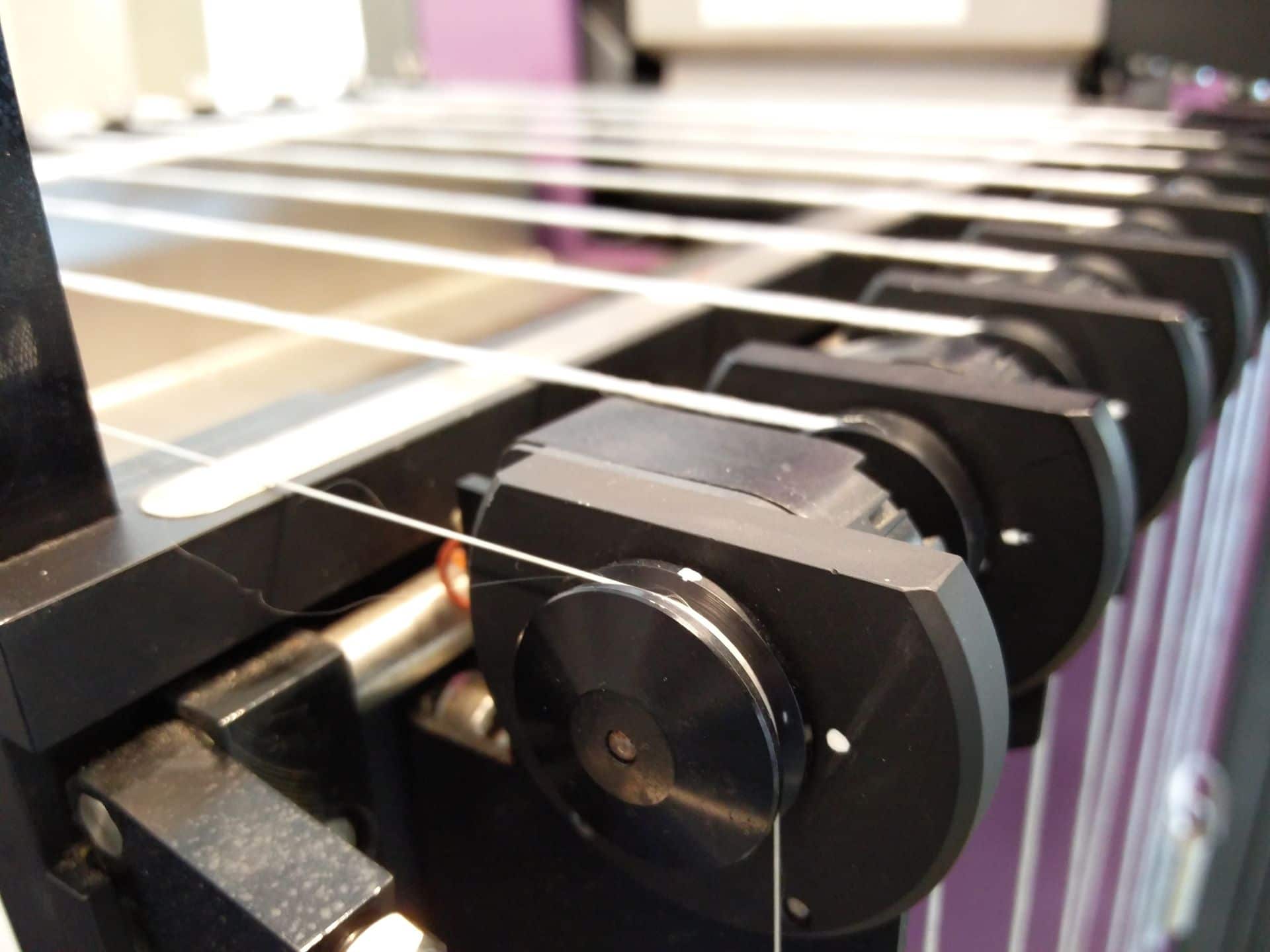

Hot air shrinkage (HAS) and Cords explained The hot air shrinkage (shrinkage under a defined yarn tension and temperature) can be measured of yarns and cords according to BISFA 2004 Ch 11 or ASTM D 4974-022. A normal procedure for PET yarns is 2 minutes at 177 °C with a yarn tension of xxx mN/tex. […]
Shrinkage hot air (SHA), free shrinkage
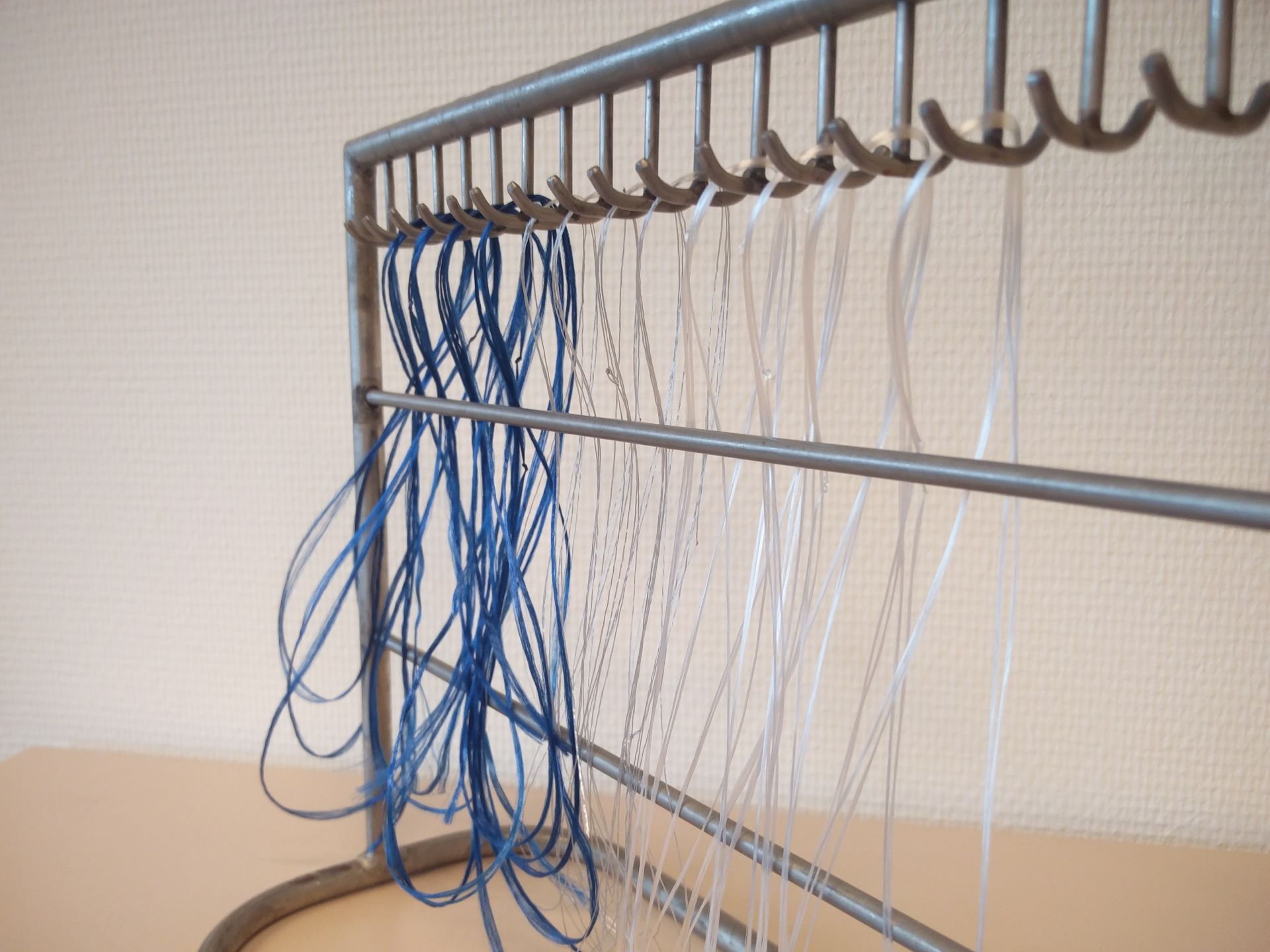

Shrinkage hot air, free shrinkage explained The free shrinkage (without any yarn tension) can be measured of yarns and cords according to BISFA 2004 Ch 10.4 or ASTM D 2259-02. A normal procedure for PET yarns is 15 minutes at 190 °C. All measurements are standard done at 3 specimen (n=3) and average values are […]